What are StableCoins? A Complete Guide
What are Stablecoins?
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies with a fixed price. Most of them peg, or attach, the price of the cryptocurrency to a fiat currency such as the dollar. This is in contrast to most cryptocurrencies which are known for their price volatility.
Why do we Need a Stable Coin?
One of the reasons the US Dollar is considered to be one of the more preferred currencies in traditional economies is that it is a known, stable currency. Most economists agree that stable currencies are necessary for a sustainable economy and economic growth. That’s the general idea behind stable coins.
There are a few sub-benefits within this as they pertain to cryptocurrencies.
1. Price Stability
As long as cryptocurrencies continue to be volatile, people, governments, and institutions will continue to view it as a speculative asset and be averse to using it for daily transactions. Why spend your bitcoin today when it will be worth so much more tomorrow, a week, or a year from now? For mass adoption of a cryptocurrency in daily transactions, you need one that is perceived as a medium of exchange. This is especially true for those using cryptocurrency to avoid their local banking system, which may have a currency with extreme volatility, or be corrupt, or poorly regulated (as opposed to those in a privileged situation to be able to use cryptocurrencies for purely speculative purposes). This is a major reason as to why the market is exploring the possibilities of a stable coin.
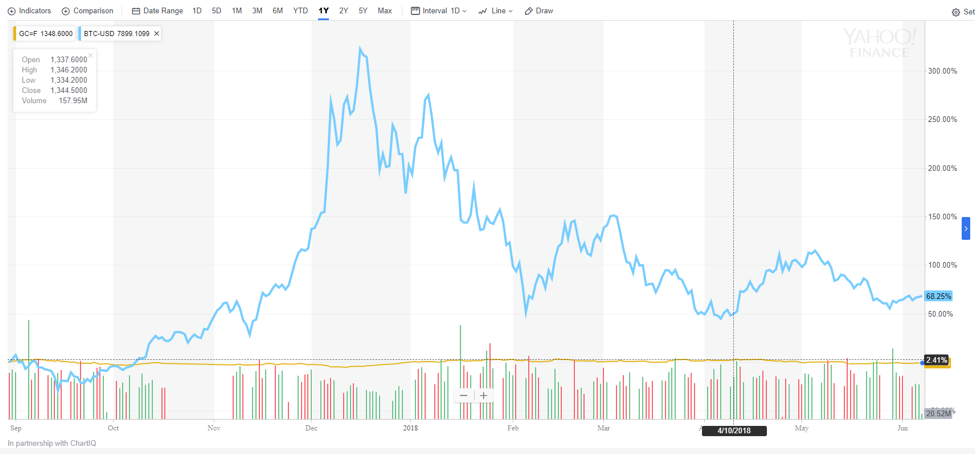
Price volatility of Bitcoin (blue) versus Gold (orange) during same year period
As you can see by the chart, the price of Bitcoin has increased by anywhere from 2% to over 300% in the last year, while the gold has fluctuated by under 1% to just under 7%.
2. Lower Inflation Rates
Stable coins are directly related to purchasing power as well. Coins with lower inflation have higher purchasing power. When inflation rates of currency is too high, spending decreases and Growth Domestic Product (GDP), or the measure of the value of all goods produced by a country, shrinks. All you need to do is take a look at countries with hyperinflation to understand this better. In Venezuela, where the current annual inflation rate is 15,657% one US dollar is worth 68,915 Bolivar. By contrast, the inflation rate in the US was around 2.5% this year and the GDP was almost 20 trillion in 2017, making it ranked the first in the world for GDP.
3. Trading in the Capital Markets
A major incentive of mass adoption of cryptocurrency is for it to replace our current financial ecosystem, but without need for a third party. Currently, cryptocurrency is not yet feasible for as a method of exchange in the traditional financial markets, as it poses to much risk due to the volatility of the coins. Although Nasdaq has stated that they are open to becoming a crypto trading exchange in the future, Nasdaq’s CEO has stated plainly that they are waiting for a more regulated market that provides a fair experience for investors. Price stability is important in the trading markets as there needs to be an incentive to trade and invest confidently long-term without constantly trying to prevent unprofitable borrowing and lending decisions.
4. Mainsteam Adoption of a Dew decentralized Internet
It is difficult to encourage adoption of applications built of the cryptocurrency protocols, especially ones connected to the derivatives or predictions market when there is so much volatility in the sector. A lot of businesses, especially smaller to medium-sized ones, don’t want to take the risk. If a fiat-free, price-stable currency existed, it can be a major incentive for greater innovation in the cryptospace.
How can a Stablecoin be Achieved?
The vast majority of stablecoins are pegged to the dollar, and there are many of them today. But in order to be successful, a stablecoin needs to be able to withstand a lot of market volatility, while at the same time not be too expensive to maintain. It also needs to be fairly easy to analyze its behavior and have transparent market conditions for traders to do so. This is especially important because it prevents market manipulation and huge sentiment swings. When stablecoins meet all of these conditions, it gives it stability and the ability to be deserving of its name.
The 3 Major Types of Stablecoins
Although there have been many attempts at designing stablecoins, each falls into one of three categories: fiat-collateralized, crypto-collateralized, and non-collateralized (seniorage shares). The term collateralized simply means that the stablecoin is being backed by, or has another currency being held as collateral in a reserve somewhere.
| Type of Stablecoin | Pros | Cons | Example |
| Fiat-collateralized | Simplest, offers 100% price stability | Need to rely on 3rd party, need to have audits to make sure right amount of collateral is being held, expensive to maintain audits |   |
| Crypto-collateralized | Better liquidity, more decentralized, transparency | Not as stable as fiat-collateral, very inefficient use of capital |   |
| Non-collateralized (seignorage shares) | No collateral required, not pegged to any currency, | Complex, unknown how resilient a coin is to devaluation, requires increasing future demand of coin |  |
Fiat-collateralized Stablecoins
Fiat-collateralized stablecoins are the simplest to understand. Each unit of the stablecoin is backed by a fiat currency, such as the US dollar. The third party, such as a bank, issues a stablecoin for every fiat coin on a 1:1 basis. In order to spend a stablecoin, the third party delivers the fiat coin to the owner and burns the stablecoin. Although this method of designing a stablecoin is the safest and simplest to understand, the disadvantage of this system is that it relies on a centralized party, such as a bank. The bank would also have to be audited to ensure that enough fiat currency is actually in reserve backing the currency. Another critique of fiat-collateralization (and collateralization of currencies in general) is that they are an inefficient use of capital, as the fiat money must sit in a reserve, not in use.
Tether is an example of a fiat-collateralized stablecoin, but it has not been able to prove that it is fully collateralized with audits.
TrueUSD is another example of a fiat-collateralized stablecoin, similar to Tether but with legal protection and transparent auditing.
Crypto-collateralized Stablecoins
Crypto-collateralized stablecoins are very similar to the fiat-collateralized approach, except the collateral is in cryptocurrency instead of fiat. In crypto-collateralized stablecoins, however, a ratio of more than 1:1 is held to back the stablecoin. This over-collateralization is necessary for absorbing price fluctuations in the collateral cryptocurrency. For example, you would need to deposit $400 of BTC to receive $200 in stablecoins. If Bitcoin were to decrease in value by 50% there would still be enough in reserve to back up the stablecoin. The major disadvantage to this approach, however, is that in the case of a serious financial crisis and crash of Bitcoin, the stablecoin would also become worthless. The over-collateralization would make the losses even greater in this case. Another critique of this method is that since crypto-currency is over-collateralized, it is an even greater inefficient use of capital than fiat-based currency.
Maker Dao (MKR)
MakerDAO, backed by Ether, is considered to be the most successful crypto-collateralized stablecoin on the market today. The first attempt at this was with BitUSD, backed by Bitshares, in 2013.
Non-collateralized Stablecoins
Non-collateralized stablecoins are not backed by any type of currency. The most common approach to this is one known as the seigniorage shares approach, which increases or decreases the supply of the stablecoin according to algorithmic principles. Smart contracts have the equivalent function as the central bank. The idea is to maintain a price of each stablecoin as equivalent to $1. When the price of the stablecoin rises to above $1, more stablecoins are minted and sold, leaving the smart contract extra profits. These profits are called seignorage, which can later be used in the event that the stablecoin drops below $1 to buy up the extra coins in circulation. If there isn’t enough seignorage available, then future seignorage is issued. However, this method is predicated on the belief that the stablecoin will continue to be of value. If the stablecoin loses value, can’t sell seignorage, and future seignorage isn’t considered valuable, the coin will lose further value and this will result in a death spiral.
Basis (formerly Basecoin)
Basis is current example of a non-collateralized stablecoin. It is a cryptocurrency aimed at keeping the price of a Basis coin at $1 – forever. It issues seignorage with a Basis bond token, to be redeemed for Basis coins in the future.
Other Stablecoin projects
| Type of Stablecoin | Logo | Description |
| Digix Gold |  |
Digix tokenizes gold on Ethereum. Every DGX= one gram of gold. |
| Arccy |  |
AAA coin is an asset-backed cryptocurrency collateralized by cash, gilts and AAA-rated credit investments. |
| Stably |  |
StableUSD are a transparent reserve-backed stablecoin for multiple blockchain protocols. |
| Sweetbridge |  |
Sweetbridge is a blockchain-based lending service and liquidity provider proposing to use cryptocurrency as collateral for asset-backed loans. |
| Havven |
|
Haven is an untraceable cryptocurrency that enables a mix of standard market pricing and stable fiat value storage without an unsustainable peg or asset backing. |
| Augmint |
|
Augmint offers digital tokens targeted to a fiat currency. |
| Fragments | 
|
Fragments is an algorithmic reserve and monetary supply policy for creating low volatility Ethereum Standard tokens |
| Carbon | 
|
Carbon is a stable cryptocurrency which closely correlates with the US dollar, achieved through an algorithmic adjustment of the coin supply. |
| Kowala |  |
kUSD is the first autonomously stabilized cryptocurrency pegged to the US dollar. |
| X8X |  |
X8X is an Ethereum-based pure utility token, functioning as a key for issuing X8Currency. |
| Globcoin |  |
Globcoin is a cryptocurrency backed by 15 different global currencies and gold. |
The Case Against Stablecoins
While the creation of a stablecoin seems like a huge boon to the cryptoworld, it also has major weaknesses.
We’ve mentioned the inefficiency of having a stablecoin backed by either fiat or cryptocurrency, but consider for a minute how difficult that would be to scale. You’d need a centralized authority or bank big enough to be willing to back the amount of cryptocurrency in the market today, which is a lot of currency on reserve, sitting around, doing nothing.
Now let’s examine a real-world controversy: Tether (USDT). Tether has not only been unable to prove transparency with audits, it has also been accused of producing tether coins that are not backed by US dollars. Case in point: 50 million tethers were minted in one week in November of last year, casting doubt that they are actually backed up by US dollars. Many have called for additional audits, and Tether has not cooperated, seeking instead to find another auditor to replace its original auditor, Friedman LLP. Bitfinex’s CEO, Jean-Louis van der Velde, is also the CEO of Tether, and the link between the two companies is also a subject of speculation. One of the harshest critics of USDT, Bitfinex’ed, has written many online accounts against the company.
If USDT is involved in widespread fraud, the ramifications are huge. It would mean that any new USDT being minted is worthless, and since USDT is used for a variety of transactions within the cryptosphere, the entire market is in danger of collapse. Some market speculators say that as people realize the devaluation in Tether, people will flee towards other cryptocurrencies or the USD, and those on tether-integrated exchanges will flee to non-tether exchanges that also offer fiat exchange. Any exchange that offers fractional reserves of any cryptocurrency, rather than full reserves, could spell serious trouble for the market, as they will suddenly require more reserves. Exchanges that offer lots of Tether, such as Bitifinex, would collapse.
Let’s not forget that beyond implications of fraud, however, all stablecoins offer varying degrees of artificial stability, and history has not proven the artificial stability of currencies to be an effective long-term solution. In the long run, it is the market that ultimately decides the price of a coin.