Vite Review – A Platform for Industrial-Strength DApps
| Name | Vite |
| Ticker | VITE |
| Token Type | Own Wallet |
| Total Supply | 1,000,000,000 |
| Category | Blockchain |
| Initial Price | $0.0639 |
| Website URL | https://www.vite.org |
| White Paper URL | https://www.vite.org/whitepaper/vite_en.pdf |
Vite’s goal is to provide a general-purpose platform that supports industrial-strength applications while at the same time delivering high throughput, low latency, scalability and security. Its reactive blockchain offers a message-driven asynchronous architecture and a DAG-based ledger. Its technology improves on existing solutions in the blockchain ecosystem, such as the ledger structure and consensus algorithm.

The Idea and the Team Behind Vite
Vite’s goal is to support industrial-strength decentralized applications, which it does through its asynchronous design and message-based architecture. This architecture delivers the advantage of high throughput and scalability. The Loopring-based protocol supports digital asset issuance, cross-chain value transmission, and inter-token transactions. It provides dual-authorization technology to prevent preemptive transactions. In addition to this, the Vite protocol allows for users pay zero fees and gas because the resource allocation is quota-based. The ecosystem also provides HTML5-based decentralized mini- programs to simplify the process of DApp development and deployment.
Vite’s founder, Chunming Liu (Charles), was formerly a senior architect at JD.com, as well as the co-founder of Coinport. He has vast experience in blockchain, distributed systems, and high concurrency systems. He has a bachelor’s in automation from the University of Science and Technology of China and a master’s in computer software and theory from the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The team’s COO, Richard Yan, has a strong traditional financial background, working in Goldman Sachs and later as the Vice President of Two Sigma’s high-frequency trading platform and Business Innovation and Growth Group. He has a bachelor’s in computer science and economics from Dartmouth and a master’s of business administration from New York University.
Frank Deng will be leading the incubator, the ecosystem development of Vite’s public blockchain. The first set of projects will be in fintech. Frank is an expert in digital and mobile marketing, with a bachelor’s degree from Tsinghua University. He was formerly in the Google Ads Operations Group and was the co-founder of Yunke Technology.

Vite Partnerships
Vite has a number of strategic partners and investors, including Loopring, a decentralized exchange protocol and automated execution system built on Ethereum. It enables users to trade assets across exchanges.
Vite recently announced a long-term strategic partnership with OK Blockchain Capital, a venture capital fund that focuses specifically on blockchain industry investment. OK Capital will play an advisory role in Vita’s development of a decentralized exchange. It will also become a major investor in the company. Other investors include Bitmain, Starwin Capital and LinkVC.
The Vite Technology
Vite is committed to improving upon existing solutions, in particular Ethereum’s system. This includes:
- Improving the state of the system — By making sure that nodes don’t have to store every transaction (making it quicker and lighter)
- Improving the state transition function — By providing more abundant smart contract programming languages.
- Improve the ledger structure –. By changing the linear ledger to a nonlinear ledger that records only partial order relations, it should speed up transactions.
- Improve the consensus algorithm — In order to increase throughput and make it less likely to have a false fork.
Ledgers
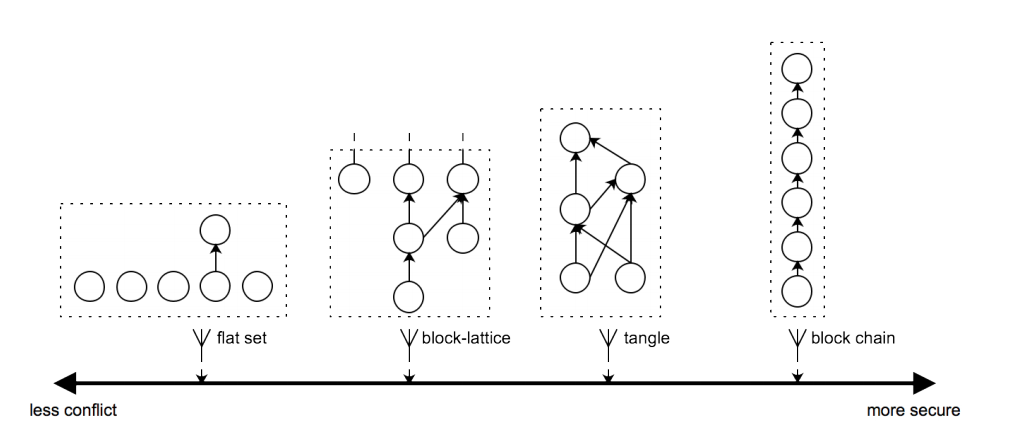
The role of a ledger is to record transactions, with particular attention to the order of transactions. The goal is for a ledger to be tamper proof as well as difficult to make false forks. Since ledgers record transactions with hashes, different orders result in different hashes. Vite’s DAG ledger structure is a composite of the four different ledger structures currently available: flat set, block-lattice, tangle book, and block chain. In addition the DAG ledger structure, they are also using Snapshot chain structure and an improved consensus algorithm.
Snapshot Chain
Think of a snapshot chain as a blockchain on top of the Vite ledger. It takes snapshots of the different state of the Vite ledger. Once transactions are confirmed in the Snapshot chain, they are then ready to go. In order to create an instance of double spending, for example, a user would have to make a hash reference in the ledger and on the snapshot chain. The difficulty of this increases the security of the technology.
Consensus
Vite has developed its own consensus algorithm, called Hierarchical Delegated Proof of State (HDPoS), which guarantees confirmation within 1 second. It is unique in that it divides consensus functions into a Local and a Global consensus. While this approach’s advantage lies in a double spend situation falling on the responsibility of only the user (and reduces the possibility of a second branch of blocks), it also means that both users must be online in order to make a transaction.
Virtual Machine
Vite has its own virtual machine, compatible with Ethereum’s virtual machine (EVM), for launching smart contracts. It has redefined the semantics of the EVM, which are available at the end of Vite’s whitepaper.
Vite’s Asynchronous Architectural Design
Vite’s unique selling point is its asynchronous design, which can be understood in three different aspects:
- Asynchronous design can be integrated into smart contracts. This means that it splits transactions into transaction pairs based on a “request-response” pattern.
- The writing and verification of these transactions are asynchronously decoupled, also supporting ultra-high throughput. That means that there will no longer be a scenario where a user sends a large number of transactions and it prevents other users from having their transactions being executed.
- Calls between contracts are also asynchronous, and message-driven, so they do not share states and communicate via messages.
Vite also allows its Vite Cross-chain Transfer Protocol (VCTP) to allow the transfer of assets between chains.
The Vite Tokens
ViteTokens are used to issue new tokens, deploy contracts, register VNS domain names and obtain resource quotas. This reduces the amount of ViteTokens in the market so that there is less liquidity. You can also think of it as having ViteTokens burned and removed from the system.
On the other hand, VitTokens are also used as incentives for node participation, increasing the liquidity of the token, which in turn dilutes these benefits. To prevent too much dilution of the value of the token, Vite will limit inflation to 3% each year.
The allocation of the total 400,000,000 tokens available for private sale is as follows:
- 20% were released on June 15
- 20% will be released on July 15
- 20% will be released on August 15
- 20% will be released on September 15
- 20% will be released on October 15
In addition to the native ViteToken, the platform allows users to issue their own tokens through a special transaction called Mint Transaction. Vite’s token issuance is like Ethereum’s, but with an important difference: it takes place within Vite’s own protocol, allowing for the balance of tokens to stay preserved in the user’s account. The need for writing code for the smart contract is no longer necessary, which decreases security risks.
The Vite Network
Vite’s goal is to develop a reactive blockchain with a message-driven, asynchronous architecture and DAG-based ledger.
Asynchronous design
Think of synchronous design as similar to telephone calls, and asynchronous design like emails. Asynchronous means more information can be transmitted and processed more quickly. This is done with Vite’s new version of Solidity. Vite’s new Solidity++’s syntax is compatible with most of Solidity, while at the same time allows for asynchronous semantics, contract scheduling, and a series of standard libraries (like string manipulation, floating-point operations, basic mathematical operations, containers, sorting, etc).
DAG
The DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) is a graph data structure with directed edges and no loops. This is what essentially makes this data structure different than other structures. Transactions are therefore grouped in accounts, with each transaction only having the ability to change the state of one single account. Sent transactions are separate from received transaction, so waiting to complete a transfer is no longer necessary before sending an additional transaction. This makes for higher performance than the traditional blockchain structure.\\
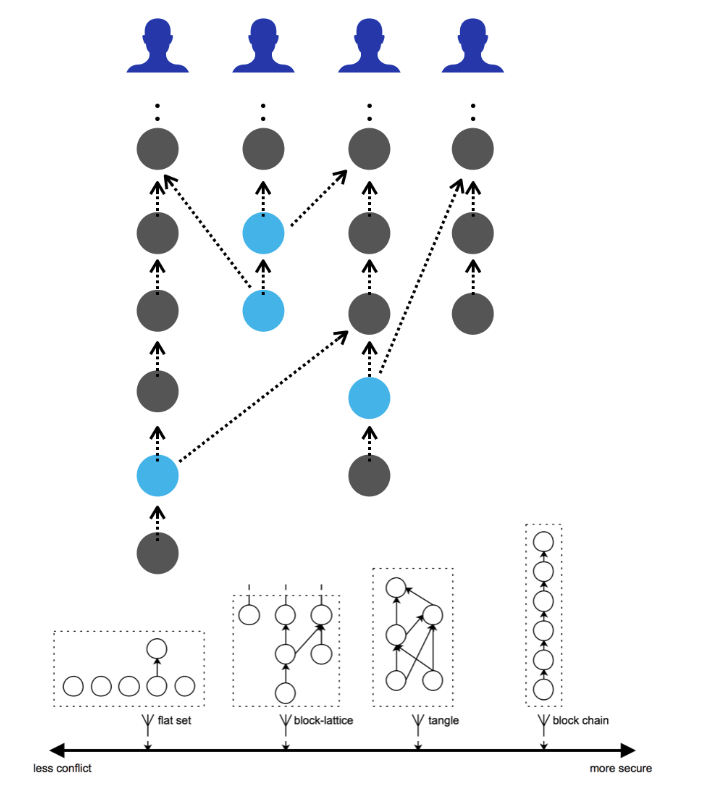
The DAG structure has a disadvantage in weaker security. As a result, Vite uses Snapshot Chain technology, an independent blockchain structure comprised of Snapshot Blocks. These Snapshot Blocks are issued by a group of delegated nodes after Delegated Proof of Stake (DPos) consensus. Delegated nodes that see forks in the account chain will decide on one and ultimately reach consensus. Snapshot Chain technology is also the global clock for the system, assisting with accurate transactions per second (TPS) metrics for each account.
The ICO and Roadmap
The company ended its private sale and will not have an ICO. It will, however, have an airdrop for community members.
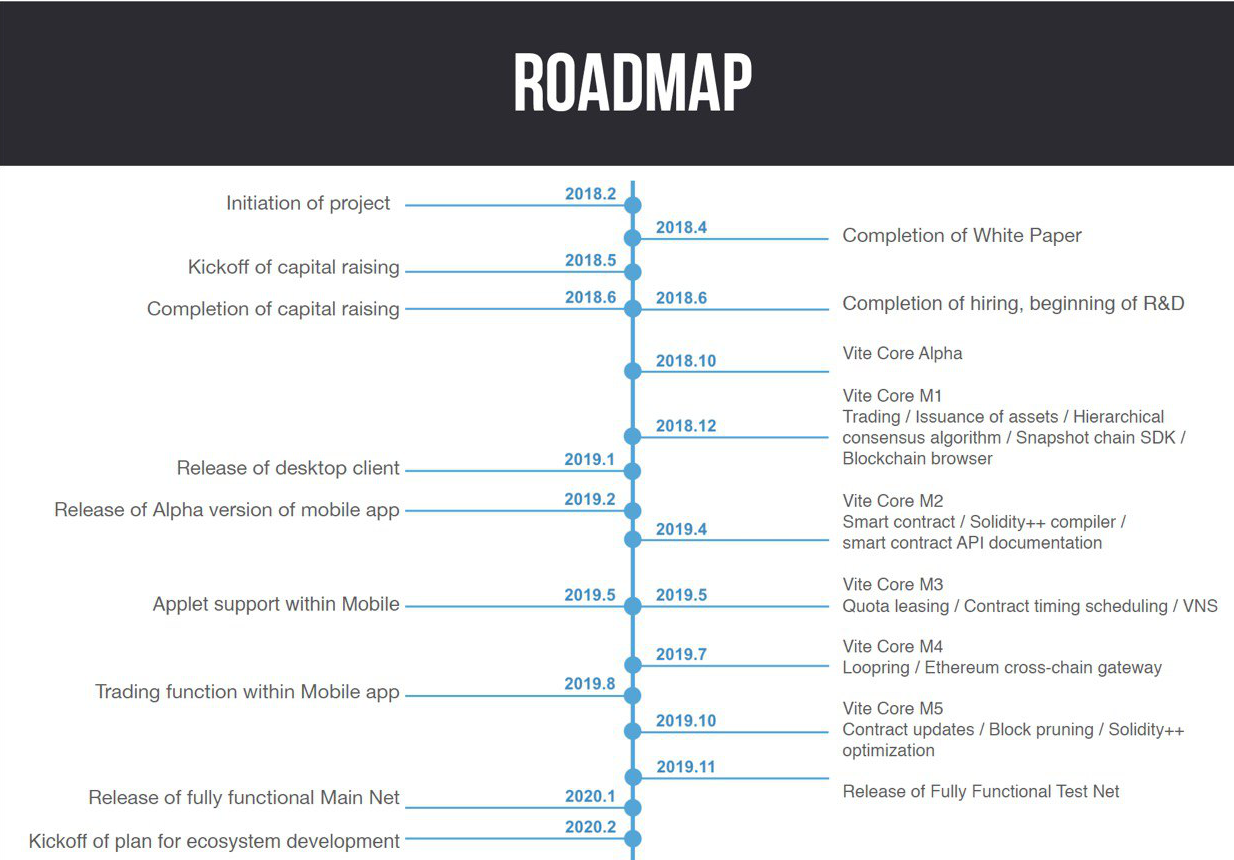
Vite has a detailed roadmap for the next few years. It includes starting Vite’s core R&D at the beginning of June and reaching Vite Core alpha by October of this year. The goal is to have completed development of the hierarchical consensus algorithm and snapshot chain and release the Vite blockchain browser by the end of the year.
The long-term goal is to have a Vite 1.0 release by January 2020