Distributed Ledger Definition
What is a Distributed Ledger?
A distributed ledger is a database unanimously shared and synchronized throughout an entire
network. By nature, distributed ledgers are decentralized and can therefore be accessed by
anyone from anywhere, regardless of geography.
Distributed ledgers can store a wide variety of data, including transactions and contracts. Each
network participant can audit the ledger, and any changes or additions that are made are
automatically implemented and copied to all participants.
Additionally, the ledger is upheld independently by each node. Records are not relayed through
a central entity, but are independently created and upheld by each node. Distributed ledgers
operate on different consensus methods which ensure that the majority of nodes agree with the
conclusions of a transaction.
The public auditability of distributed ledgers adds a level of security and transparency that isn’t
present with other databases. The public nature of distributed ledgers also means that
transactions are immutable and irreversible.
What’s more, there is no need for a central authority who maintains and controls the ledger. The
direct interaction between nodes saves on transaction times and costs, in addition to providing
greater network security.
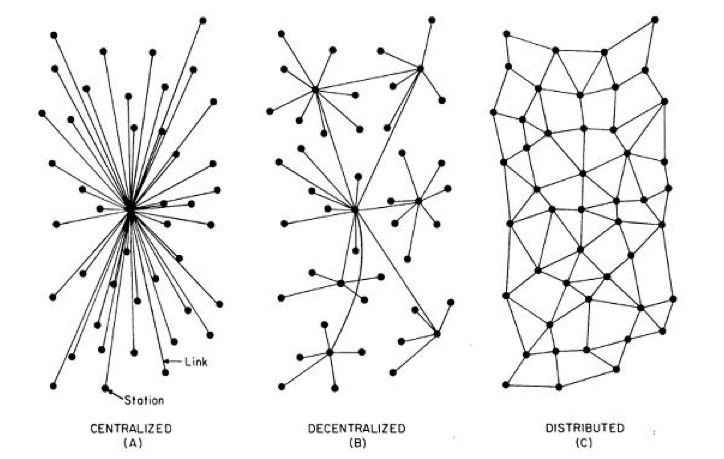
Why Are Distributed Ledgers Used?
Distributed ledgers provide greater security than centralized databases because cyber attackers
must attack all distributed nodes at once to be successful. The chances of launching a
successful attack is much higher if only one target must be taken down.
Because each participant has a copy of the ledger, it is also impossible for a single party to
make any changes to the network’s record or operations. The changes would be proposed, then
immediately rejected by ledger consensus.
Distributed ledgers greatly cut down on transaction time and costs, especially for cross-border
or global transactions. The ability to send assets from anywhere in the world to anywhere in the
world in a quick and efficient manner is a huge of advantage.

